Encephalitis: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Encephalitis is a disease that consists of inflammation of the brain. It is a pathology that is usually caused by a viral infection, although it can have many other causes. In fact, most of the time it is a complication of other infectious diseases.
Fortunately, encephalitis is rare. In recent years, its incidence has been significantly reduced, thanks to widespread vaccination and under official calendars. Still, the most affected population is children.
It is estimated that there are between 5 and 10 cases per 100,000 children. Unfortunately, most of them take place during the first year of life. It is a complicated situation that puts the life of those who suffer it at risk.
Both the causes and the symptoms can be confused, and it is essential to detect the pathology early. Therefore, in this article we explain what encephalitis consists of, its causes, symptoms and treatment.
What Causes Encephalitis?
As we have already mentioned, encephalitis consists of inflammation of brain tissue. It is a pathology that can have multiple causes, although the vast majority of cases are caused by a virus. However, it can also be a bacterial infection.
When the infection occurs directly in the brain, it is called primary encephalitis. However, it may be the case that the infection begins in another part of the body and that, due to migration, it ends up affecting the brain: it is secondary encephalitis.
In children, the viruses directly involved are rubella, measles, and mumps. Fortunately, there are vaccines against these agents. Other causes are:
- Herpes virus: both herpes simplex, Epstein-Barr or chickenpox can cause it.
- Rabies virus: usually transmitted by animal bites.
- Enterovirus: like poliovirus.
- Bacterial meningitis: not properly treated.
- Parasites
Importantly, encephalitis itself is not a contagious disease. What must be taken into account is the cause that has produced it. Also, as we mentioned before, it can be the result of other processes, such as cancer.
What are your symptoms?
Considering that most cases are caused by a virus, the initial symptoms can be very nonspecific. For example, it is typical that there is fatigue, muscle pain and headache. In addition, fever often occurs.
When the pathology progresses, the symptoms are usually more intense. There may be seizures, loss of consciousness, and even trouble speaking. It also happens that some people lose sensitivity in areas of the body.
In infants, it can be very difficult to appreciate the symptoms. Children are often irritable, vomit, or not eat properly. In the most severe cases, a coma is reached. If left untreated, encephalitis leads to death.
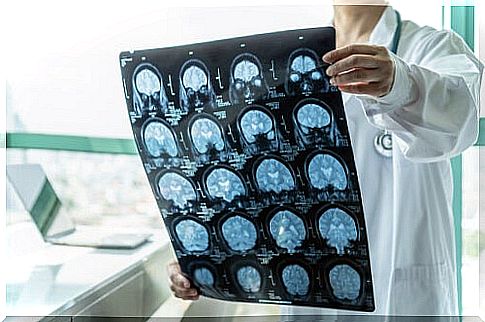
What is the treatment for encephalitis?
In order to diagnose this disease, different tests and studies are needed. First, blood and urine tests are essential. This allows to guide the diagnosis and the possible causes.
Typically, an MRI or CT scan is done to look at the brain. Sometimes a lumbar puncture is necessary. With it, cerebrospinal fluid is extracted which, when analyzed in the laboratory, can confirm the cause.
To treat encephalitis, the first thing is to keep the person stable and at rest. Treatment includes pain relievers such as acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
What to do with the symptoms of encephalitis?
Although in children it is a pathology that is difficult to diagnose, some signs can guide suspicion. In adults it will be the presence of severe headache and fever, plus some alteration in cognitive functions.
There are some encephalitis viruses for which there is a specific treatment. However, this is not always the case. It is very important that, before any symptoms, you consult a doctor. Encephalitis is life-threatening.